Describe the Processes Used to Produce Light in a Laser
In NIF as in most large lasers intense flashes of white light from giant flashlamps pump electrons in large slabs of laser glass to a higher-energy state that lasts only about one-millionth of a second. Second the light released from a laser is coherent which means that it is ordered and controlled.
Laser Technology Definition Applications And Challenges Physics Metropolia Confluence
Some light waves are reflected between two mirrors and cause more atoms to emit light resulting in a narrow intense light beam.
. Laser stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The acronym LASER stands for Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. Laser of different power and application can be produced by using different materials.
Attempts to describe the origin of the emission and absorption lines ie the. Researchers have demonstrated the worlds first metasurface laser that produces super-chiral light. Oppositely natural light is a combination of many colors.
A Trbecularplasty b Lithotripsy c Viscocanalostomy 17 The National Ignition Facility will use what type of laser for fusion power experimentation. Because of this coherence a large amount of power can be concentrated in a narrow space. The liquid dye lasers use liquid dyes like rhodamine in a liquid solution as their medium.
First lasers are monochromatic or having only one color. Pulsed lasers have very high intensities because the laser intensity is concentrated in a very short time duration. The photons produced are equivalent to waves of light whose crests and troughs line up in other words they are in phaseand thats what makes laser light coherent.
Atoms in the laser tube absorb light from a flash tube and emit light at one wavelength. The population inversion is required for laser operation. These lights have no existence in nature.
The light source is used to stimulate the laser rod which is composed of atoms of a lasing media that absorbs certain wavelengths of light from the light source. In these lasers the electrons are excited either by an arc lamp flash lamp or another laser. 18 Atoms in the laser tube absorb light from a flash tube and emit light at one wavelength.
The lights can be produced through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. Unlike naturally occurring light laser light is artificially produced. A Visible b Ultraviolet c Infrared 16 Laser energy is used to break up kidney or gallstones in process called.
What is the process used to produce light in a laser. We may conclude that laser action is preceded by three processes namely absorption spontaneous emission and stimulated emission - absorption of energy to populate upper levels spontaneous emission to produce the initial photons for stimulation and finally stimulated emission for generation of coherent output or laser. A laser light has three properties that make it unlike any other light source.
20 Eradiant Ein -. The laser cavity contains a laser rod where the radiation is generated. Stimulated emission in lasers makes electrons produce a cascade of identical photonsidentical in energy frequency wavelengthand thats why laser light is monochromatic.
Light with ultra-high angular momentum. Lasers use artificial light. 19 read CDs surgery light shows pointers.
Population inversion is the process of achieving greater population of higher energy state as compared to the lower energy state. Liquid dye lasers can produce a broader band of light frequencies as compared to solid-state or liquid lasers and are used in a variety of applications. Ruby laser is an example of solid state laser in which ruby crystal is used as medium for the generation of laser beam.
External sources of light examples flashlamps or another laser - PUMPING The output of the laser light can be a continuous wave cw if the pumping is continuous or pulsed if the pumping is pulsed. Light bounces back and forth between the mirrors passing through the gain medium and being amplified each time. It is different from conventional light in three ways.
The media of the solid state lasers are produced by doping a rare element into a host material. That materials when heated in flames or put in electrical discharges emit light at well-defined and characteristic frequencies was known by the mid-19th century. Typically ultraviolet light is used to transfer a.
In laser a technique called stimulated emission is used to produce light. This laser pulse stimulates the electrons to drop to their lower or. But there are defining properties to laser light.
Next laser light is directional which means that it goes in a one-pointed direction. Lasers are produced by generating light from a high-intensity light source inside a reflective laser cavity. In integrated circuit manufacturing photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate such as a silicon wafer to protect selected areas of it during subsequent etching deposition or implantation operations.
Laser is a device used to produce very intense highly directional coherent and monochromatic beam of light. Population inversion technique is mainly used for light amplification. First lasers are monochromatic which means they produce light of one wavelength or of one color.
15 The Eximer laser produces light with what wavelength. A small pulse of laser light tuned to the excited electrons energy is directed through the glass slabs. Again natural light is the opposite as it.
It is a device which produces lights. The study of the emission and absorption spectra of atoms was crucial to the development of a successful theory of atomic structure. Typically one of the two mirrors the output coupler is partially transparent.
Thus light generated by laser is highly coherent. Some light waves are reflected between two mirrors and cause more atoms to emit light resulting in a narrow intense light beam. In these types of laser gases are used as the medium to produce lasers.
The most common type of laser uses feedback from an optical cavity a pair of mirrors on either end of the gain medium. The commonly used gases are He-Ne argon and Co2.

Laser Beam Welding Working Equipments Applications Pdf
Laser Beam Machining Principle Working Advantages And Disadvantages
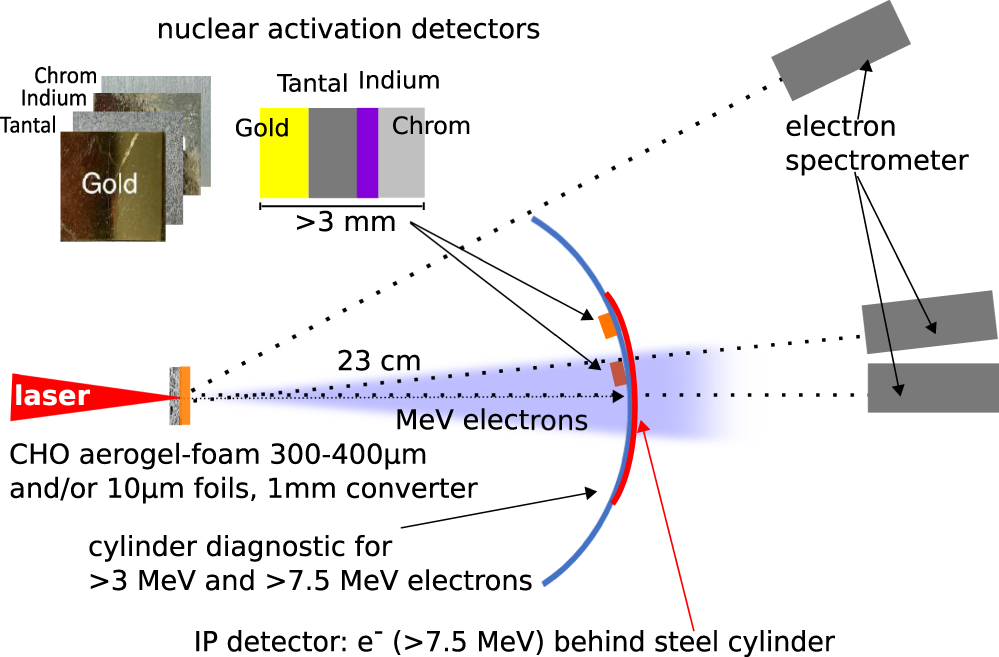
Forward Looking Insights In Laser Generated Ultra Intense G Ray And Neutron Sources For Nuclear Application And Science Nature Communications

Laser Definition Acronym Principle Applications Types Britannica

Pin By Liselotte Leijten Deppenbroek On Heijerman

Focused Laser Beam An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Importance Of Laser Technology What Are Lasers Used For Today
What Is A Laser How Is Laser Technology Used
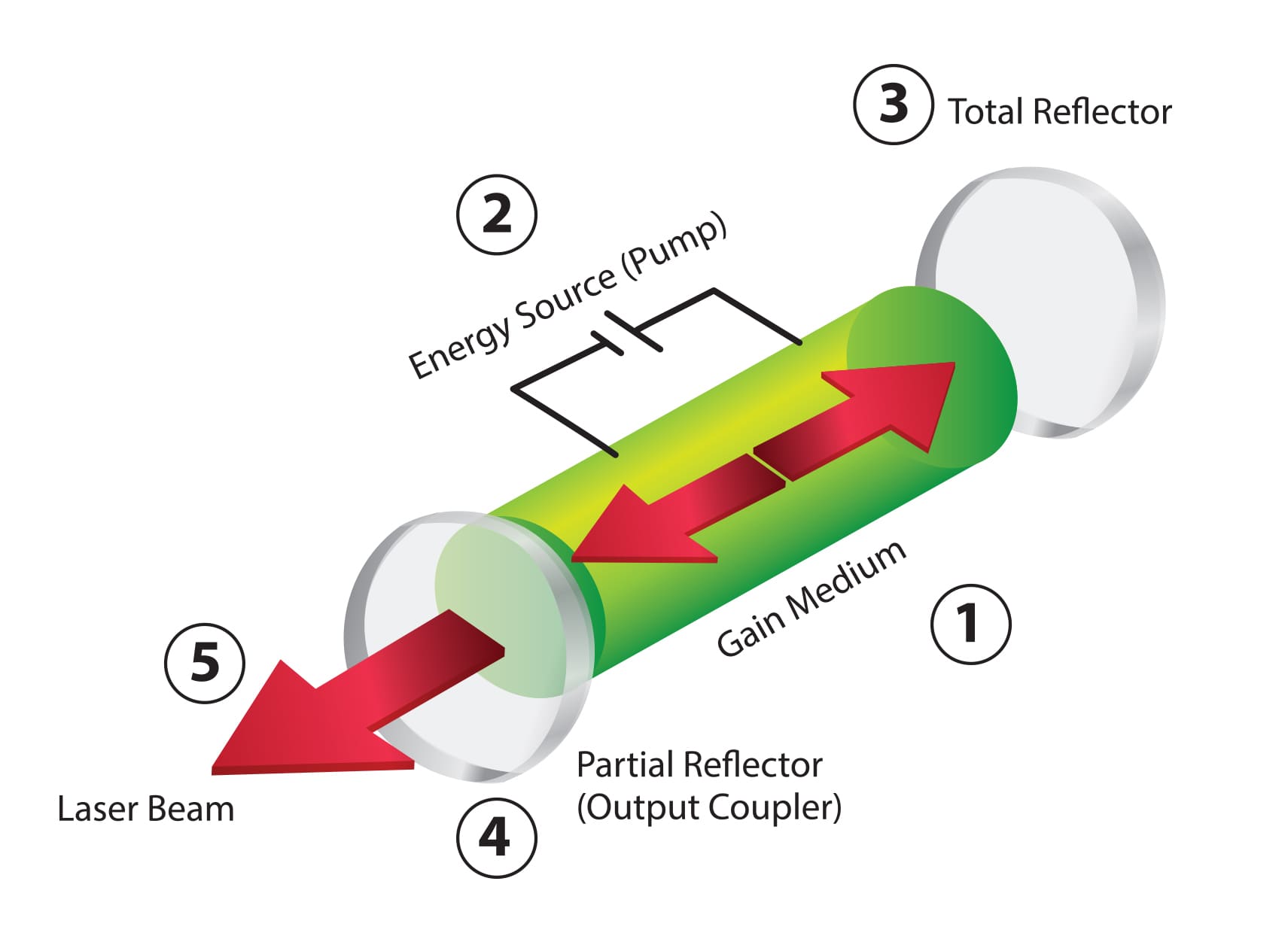
What Is A Laser How Is Laser Technology Used

Ultra Intense Laser Stops Electrons Travelling At Near Light Speed For First Time Mimicking Black Holes The Independent The Independent

Fundamentals Of Laser Safety Laser Safety In Specialized Applications

Selective Laser Melting Wikipedia

Laser Cooling For Quantum Gases Nature Physics
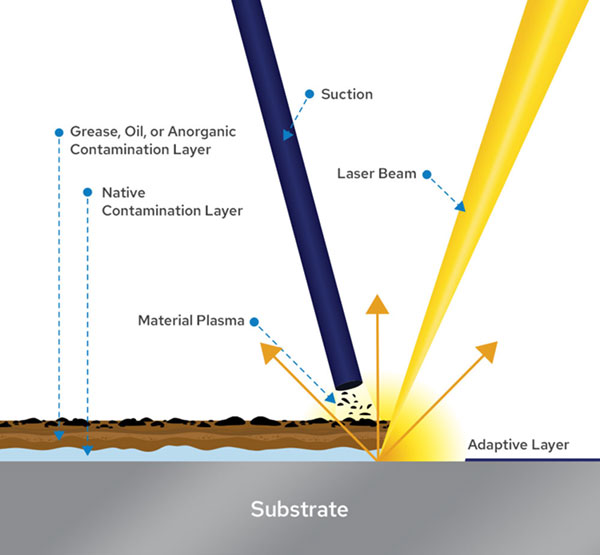
How Laser Cleaning Works Adapt Laser

Laser Processing Technology Application Development Machinemfg

Laser Definition Acronym Principle Applications Types Britannica

Nif S Guide To How Lasers Work

Pin On Sheet Metal Work And Sheet Metal Fabrications In Eastleigh Hampshire
Laser Technology Definition Applications And Challenges Physics Metropolia Confluence
Comments
Post a Comment